Hydroponics, the practice of growing plants without soil, has become increasingly popular in recent years as a sustainable and efficient method of agriculture.
However, managing a PPM chart for Hydroponics can be complex. It requires careful monitoring of various factors such as nutrient levels, pH, and water quality.
In this article, we will learn the basics of using a chart, maintaining the PPM ranges, and calculating the values with EC (electrical conductivity). So, let’s dive in without wasting any more time!
Contents
Understanding the PPM Chart for Hydroponics and its Basic Values
PPM is an integral unit of measurement in a hydroponics system:
- It stands for “parts per million” and determines the concentration of fertilizers in the storage tank.
- PPM refers to the milligram concentration of too many nutrients in 1 liter of hydroponics water.
- Maintaining a stable PPM level is essential for healthy plant maturation.
- Over or underfeeding plants can have detrimental effects on their growth and health.
Therefore, keeping a close eye on the PPM levels in your hydroponic setup is important.

Regulation of pH Level
In a hydroponics system, tap water and nutrients are mixed to provide a nutrient-rich solution to plants. However, certain particles in the mixture can harm plants, especially if the pH level is too low.
- PPM and pH levels should be regulated to ensure the well-being of your plants.
- If the PPM and pH levels are not balanced, it can be hazardous for your plants.
- If the pH level is too low, even an accurate PPM value may result in high levels of heavy metals in the plant’s meals.

Common PPM Reading to Help Understand the PPM Chart
Here’s an example of a common PPM reading that can help you understand how to make a PPM chart:
- Seedlings: 100- 250
This stage does not require too many nutrients, so it’s suggested not to add particles here.
- Vegging Cycle (First Half): 300-400
You achieve the vegging cycle right after transplanting the seedlings, so only add a few nutrients.
- Vegging Cycle (Second Half): 450-700
The growth begins in the second half of the feeding cycle; you should add more nutrients to all the plants.
- Flowering (First Half): 750-950
The growing process speeds up at this stage, and the plant requires some extra nutrients.
- Flowering (Second Half): 1000-1600
Start giving some additives to the plants at this stage. As a result, they will start taking more food (nutrients) than before. This stage is also the max PPM during the process.
- Harvest Starting Period: Bring the PPM reading close to the zero
It’s time to flush the plants. Remember that there will not be too many particles here.

Maintain the PPM Range to Keep Plants Healthy
Maintaining the PPM chart range is crucial as it can flourish or destroy your plants. If the PPM drops considerably low for the required plant accidentally, it stops taking enough nutrients and eventually dies.
First, we will look at the PPM ranges for vegetables and their growth season:
Vegetable | Season | PPM Range |
Artichoke: | Spring | 560-1260 |
Beans: | Spring | 1400-2800 |
Beetroot: | Spring | 1260-3500 |
Lettuce: | Summer | 560-840 |
Okra: | Summer | 1400-1680 |
Radish: | Summer | 840-1540 |
Carrots: | Fall/Autumn | 1120-1400 |
Cauliflower: | Fall/Autumn | 1050-1400 |
Celery: | Fall/Autumn | 1260-1680 |
Asparagus: | Winter | 980-1260 |
Spinach: | Winter | 1260-1610 |
Turnip: | Winter | 1260-1680 |
Next, let’s have a look at the PPM ranges for some famous herbs:
Herb | Season | PPM |
Basil: | Summer | 700-1120 |
Chives: | Spring | 1260-1540 |
Parsely: | Spring | 560-1260 |
Rosemary: | All-Year-Around | 700-1120 |
Sage: | Spring/Fall | 700-1120 |
Thyme: | Spring/Summer | 560-1120 |
PPM Level Adjustments for Perfect Nutrient Solution
It is crucial to adjust the base level PPM to prepare the water for plants since they absorb nutrients from it:
- This adjustment is necessary because the source of base water is usually tap water, which contains other impurities and minerals.
- Once the PPM level is adjusted, any required ingredients can be added to the water to initiate the process.
- It is important to monitor the PPM level carefully as the number of particles increases.
- Water and particle readings can give a more accurate PPM meter value.
Therefore, it is recommended to keep an eye on the PPM graph to ensure that the water has the optimal nutrient level for the plants.

1. Pure Watering Solution
When there are more particles in the water, the probability of a PPM imbalance increases, thus hurting plant growth.
- This issue is easily avoided by purifying the water and removing excess particles using a charcoal, carbon filter, or reverse osmosis unit.
- While tap water can contain beneficial minerals for plants, ensuring they are in the right proportions is crucial.
- It is also important to remember that using purified water can affect the nutrient intake of plants.
- May require a higher nutrient input during and after the vegging period.

Recommendation
Therefore, we recommend using filtration early in the plant’s development. This will help to maintain the PPM levels at an optimal range throughout the proper growth/feeding cycles.
- By filtering the water early on, the PPM levels will be lower, making it easier to adjust the nutrient levels according to the plant’s specific needs.
- This will result in healthier and more robust plant growth, essential for achieving high yields and quality crops.
- Overall, paying attention to the PPM levels and using proper filtration techniques makes a significant difference in the success of your plant maturation.
2. A Quick Fix When Necessary
When the PPM level rises, the Hydroponic system needs to be refilled with clean water with a suitable pH. Monitoring the PPM graph regularly is essential to maintain the PPM levels at an optimal range.
This can help you to identify any imbalances or fluctuations in the pH and PPM levels, allowing you to take corrective action quickly. However, if this issue persists, it is important to try different approaches, such as:
- Adjust the nutrient levels
- Use different fertilizers
- Implement a new filtration system

3. Stabilize the Low Reading
A low PPM value indicates that your plants may require more nutrients to support their growth. In this case, supplementing the solution with the right nutrients can help to bring the PPM level back to normal.

The Most Common Measurements on PPM Meter
Hydroponic gardeners widely use EC as the primary measuring method for Hydroponics. Since it is the most straightforward and reliable way to determine the solution’s total mineral load.

However, PPM and TDS meter measurements also pinpoint nutrient-related issues:
- Commercially available PPM meters measure EC and then convert the readings to PPM, making EC the preferred unit of measurement.
- The PPM reading on the meter may vary, having access to both units.
- It is helpful, especially since nutrient providers express nutrient amounts in PPM and EC values.
What Do Americans Prefer?
While American hydroponic growers prefer PPM for measuring fertilizer levels, EC is the standard worldwide. Keep your plants healthy and ensure they receive the nutrients to thrive by regularly monitoring your hydroponic system PPM and EC levels.
Additionally, you can head to this video to better understand the TDS (total dissolved solids), PPM, and EC terms.
Preferred PPM Levels for Hydroponic Plants
Since different plant species require varying amounts of nutrients, growing plants with similar nutrient requirements in the same hydroponic system is important. To determine the optimal PPM levels for your hydroponic system, several factors must be considered that are described below:
1. Farmer’s Preference
Many hydroponic farmers use multiple systems to accommodate the different fertilizer concentrations needed for various plant species.
A PPM level between 1,200 and 1,500 is ideal for most plant species, starting at the lower end of the range is best and gradually increasing if necessary.
- This will allow you to precisely adjust the fertilizer content to meet the specific needs of your plants.
- It’s also essential to adjust the PPM range according to the different growth phases of your plants.

2. Provide Nutrients According to the Requirements
Different stages of plant development require varying nutrient concentrations, so monitoring and adjusting the PPM range is crucial. Understanding these variations in nutrient requirements is highly important.
It will enable you to provide your plants with the appropriate nutrients at the right times during their proper growth and development.

Hydroponics PPM Chart
The Hydroponics PPM chart below shows some of the most common crops and their PPM requirements at different growth stages.
Crop | Early Growth | Mid-Growth (Pre-Fruiting) | Flowering and Fruiting |
Strawberries: | 800 – 900 PPM | 800 – 900 PPM | 400 – 500 PPM |
Tomatoes: | 300 – 500 PPM | 500 – 900 PPM | 1400 – 2500 PPM |
Cucumbers: | 300 – 500 PPM | 800 – 1000 PPM | 1190 – 1750 PPM |
Kale: | 300 – 500 PPM | 560 – 840 PPM | 900 – 1500 PPM |
Lettuce: | 100 – 150 PPM | 200 – 500 PPM | 560 – 840 PPM |
Understanding the Terms and Calculating PPM
PPM or parts per million refers to the concentration of a specific substance. For instance, in hydroponic farming, PPM determines the number of nutrients or total dissolved solids (TDS) in the water solution.
- Several metrics are considered to arrive at this measurement, such as the solution’s electrical conductivity (EC), which measures its ability to conduct electricity.
- The solution’s pH level is crucial as it determines the solubility of nutrients in the water.

pH (Potential Hydrogen)
The pH scale is a measure of the acidity or basicity (alkalinity) of a substance. It ranges from 0 to 14, with a pH of 7 being neutral. Less than 7 indicates acidity and greater than 7 indicates basicity (alkalinity).
- In hydroponic farming, pH measurement is crucial as it helps determine nutrient concentration availability in the water solution.
- Nutrients are most readily available to plants within a specific pH range.
- Any deviation from this range can result in a nutrient burn or toxicities.
Therefore, maintaining the correct pH range is essential for optimal plant health.

EC (Electrical Conductivity)
Electrical conductivity (EC) is another important measurement in hydroponic farming. It provides information about the water solution’s quality and quantity of nutrients. It is typically presented in milliSiemens per centimeter (mS/cm) or microSiemens per centimeter (µS/cm).
- One mS/cm is equivalent to 1000 µS/cm.
- A higher EC value indicates a higher concentration of nutrients in the water solution.
- The specific target range will vary depending on the crop being grown and the growth stage of the plants.

How to Read and Calculate PPM?
Now that we understand PPM, pH, and EC measurements in hydroponic farming, we can discuss how to take a reading and adjust the nutrient solution accordingly. A truncheon meter is one of the simplest and most convenient ways to calculate PPM readings. To take a reading:
- Hold the truncheon probe tip in the solution for at least 2 minutes, completely submerging the whole tip.
- The truncheon meter will then display the PPM value. Once you have a reading, you can adjust the solution as needed.
- Add fresh water or use a carbon filter to lower the PPM.
- You can add more nutrients to raise the PPM, but sticking to a strict nutrition plan is essential to avoid over-fertilization and toxic shock to the plants.
- After making adjustments, take another PPM value to ensure that the desired range has been reached. Rinse the truncheon meter with clean water once testing is complete.
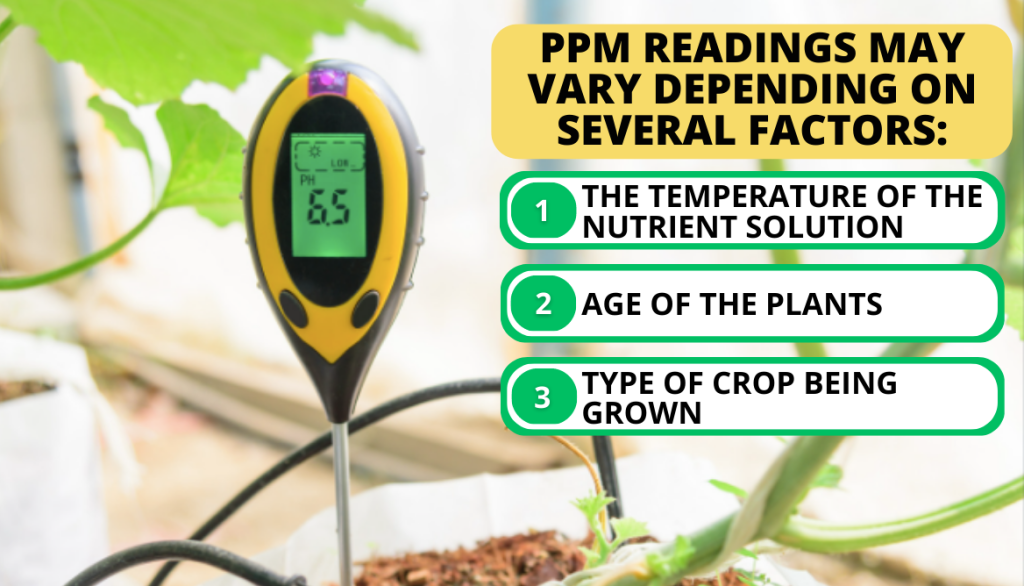
It’s important to note that PPM readings can vary depending on several factors, such as:
- The temperature of the nutrient solution
- Age of the plants
- Type of crop being grown
Therefore, it’s recommended to take PPM reading regularly to ensure the solution is properly balanced for the plants’ specific needs.
FAQ
What is the perfect PPM for Hydroponics?
The perfect PPM for Hydroponics should range between 800 to 1500 as the plants consume nutrients and water. Changing the nutrient strength in the hydroponic reservoir.
What happens if PPM is too high in Hydroponics?
If PPM is too high in Hydroponics, it can become toxic and lead to the plants’ death. Therefore, hydroponic growers must monitor the PPM range in their systems closely. It is important to ensure optimal levels to facilitate plant development.
What is the recommended PPM for vegetables?
The recommended PPM for vegetables is between 800 to 850. As the plants progress to the mid-stage vegging phase, they should be increased to 850 to 900 PPM. In the late-stage vegging phase, it should be increased to 900 to 950 PPM.
How much ppm is too much?
Any PPM exceeding 1500 is too much. The ideal PPM level is generally between 500 to 1000 for most plants during the vegetative growth stage. It is between 1000 to 1500 ppm during the flowering stage.
What is pH vs ppm?
The term pH pertains to the hydrogen ion concentration in water, indicating whether it is excessively alkaline or acidic. Meanwhile, parts per million (PPM) denotes the level of soluble substances and minerals dissolved in the water used for watering.
Conclusion
With the increasing demand for sustainable food production and the limitations of traditional agriculture, Hydroponics offers an innovative and efficient solution. So, whether you are a seasoned hydroponic grower or just starting, include a PPM chart for Hydroponics in your arsenal of tools for successful cultivation.
Have you ever tried hydroponic cultivation before? If so, what tools or techniques have you found most effective in achieving healthy plant growth? Enlighten us with your valuable answers in the comment section below!
- PPM Chart for Hydroponics: Level Adjustments Guide for 2023 - April 2, 2023
- Kawasaki FR vs FS: Discussed with Key Features, Benefits, and 10 Specs - March 10, 2023
- Best Tiller for John Deere 1025R: 2023 Guide with 5 Factors - March 9, 2023

![PPM Chart for Hydroponics: Level Adjustments Guide for [Year]](https://thisgardener.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/PPM-Chart-for-Hydroponics-740x423.png)
Add comment